
10/09/2009
Jobless growth. That is a term that makes one pause. With an
economy where the consumer comprises about 70% of the Gross Domestic Product
(GDP), it is hard to imagine how an economy can grow without more people
working. Yet jobless growth is what the
As of October 2009, the unemployment rate in the
Let’s look at some facts from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) to provide a proper foundation before discussing the prospect for job growth. By the way, all the tables and charts for this article are from the Bureau of Labor Statistics Labor Force Statistics from current Population Survey for October 2009.
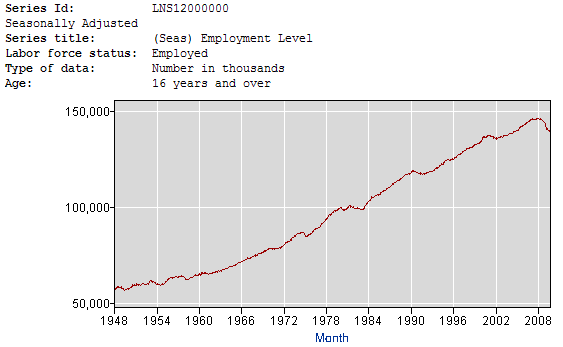
According to the BLS, there are 138.3 million jobs in
October 2009 in the

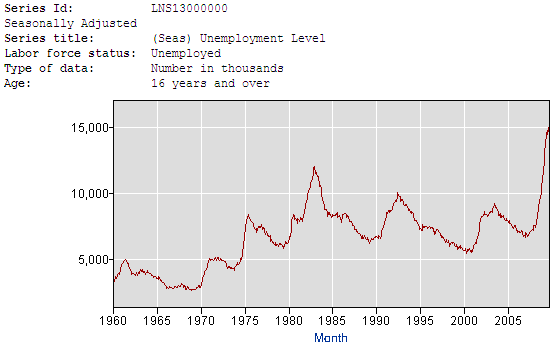
A 10.2% unemployment rate means there are 15.7 million people count as unemployed. As you can see this number continues to climb and is up significantly from a year ago. According to the BLS “Persons are classified as unemployed if they do not have a job, have actively looked for work in the prior 4 weeks, and are currently available for work.”
Below are the chart and the table displaying the number of people classified as unemployed. As you can see, we are reaching unprecedented levels.
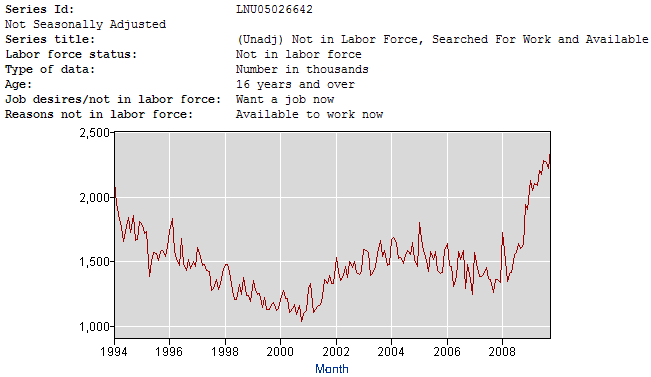
The 10.2% does not count the number of people who have not actively looked for a job in the last four weeks. In October 2009 there were 2.4 million people “marginally attached” to the labor force. These discouraged workers are not considered part of the labor force even though they wanted to work or had looked for a job in the prior 12 months. The government does not count these people as unemployed since they have not looked for work in the last four weeks.
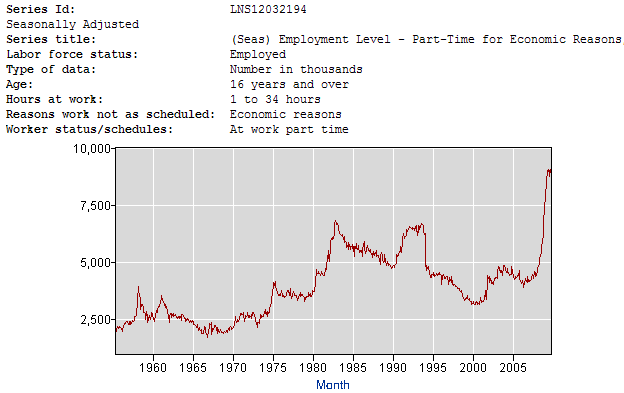
Next, there are 9.3 million people working part time who want full time work. Many of these people are working in jobs well below their training and skill level. These individuals are working part time as their hours have been cut back of they have been unable to find full-time work.
Adding all the marginally attached workers to those counted as unemployed we reach the 17.5% of people who are out of work, have given up looking for work or are working part time and want full time work. You might have heard about this U6 unemployment level. It is a more realistic measure of the real unemployment problem the country faces.
That is the bad news. What are the prospects for job growth to meet the needs of workers who are unemployed and who will be joining the work force over the next five years?
As of October 2009, the total civilian labor work force was 153.975 million. This number has been flat for more than a year as the number of discouraged workers increases. Remember discouraged workers are not counted as unemployed or part of the labor force, so they are not part of this number.
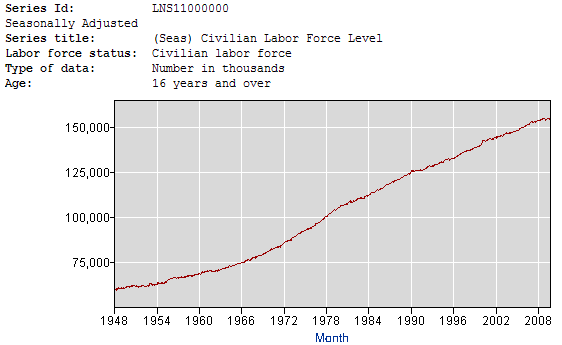
Each month 125,000 to 150,000 people join the workforce. This means the economy must produce 1.5 to 1.8 million new jobs each year to keep up with the growing work force.
For October 2009, the as reported average workweek was down to a record low of 33 hours per week, from a pre recession level of 33.8 hours worked per week. This is another sign the demand for work is weak. If you do the math, it will take the equivalent of hiring 3 million people to get back to the pre recession level of 33.8 hours worked.
Let’s assume the economy starts to produce net new jobs by the beginning of 2010. How many jobs per month must the economy generate to bring the unemployment number down to 5% by 2014?
Starting with the 157 million in the work force as of the end of 2009, we add 1.5 million new workers or 7.5 million over the five years, giving us 164.5 million in the labor pool.
Five percent of 164.5 million is 8.2 million unemployed at the beginning of 2014. This would be substantially down from the 15.7 million that were part of the 10.2% unemployed in October 2009.
To get the number of jobs the economy must product we subtract 8.2 million from 164.5 million gives us 156 million jobs by the end of 2014. As mentioned above there are 139 million jobs today. This means the economy must produce 17 million new jobs in the next five years (156 million – 139 million). 17 million jobs is an average of 3.4 million jobs per year or 283,333 jobs per month.
For a frame of reference, let’s look at what the jobs the economy produced in the last ten years to see if it is possible to generate this many jobs. The table below from the BLS shows the net change in jobs created or lost by month since 1999.
The highest twelve-month sequential rate of job creation during this period was 2.755 million jobs per year. In 1999 at the height of the one of the greatest periods or economic growth in many years, 2.246 million jobs were created. Moreover, only ten months did the number of jobs created exceeded the average number needed to reach 5% unemployment by the end of 2014.
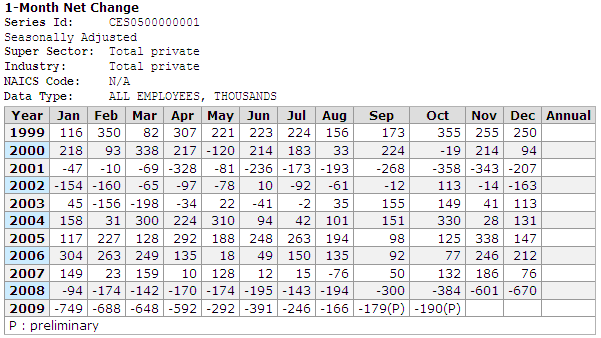
The
We can hope that the economy will be able to generate enough jobs to drive unemployment down to below 5% and to provide opportunities to the discouraged, marginally attached, and part-time workers. But we cannot count on hope. More likely, we will witness a jobless growth scenario that will leave many people unable to find meaningful work.
As investors, we will face the prospect of high and chronic unemployment and under-employment for years to come. A jobless growth economy will limit the ability of the economy to expand. Worse, we might see solid job growth among the well-educated and total lack of job growth among those with high school or less education.
However, not all is lost. As in any economy, there will be sectors and industries that will offer better growth opportunities. We are witnessing a change in the labor force that places a premium on higher skills and education. New technologies and methods of work will be the order of the day. Global competition and trade are creating new economies that offer opportunities that did not exist before. Companies that can take advantage of these openings will offer investors significant returns. The transition to the wireless internet and the Web 2.0 will support technology companies that provide the hardware, software, and services.
Consistent high unemployment will cause the government deficit to remain high helping to devalue the U.S. dollar further. As the value of the dollar falls, it will encourage the value of commodities to rise. Higher commodity prices offer investors additional returns. A weaker dollar is a positive for exports. Any company that will benefit from a growing export sector will benefit.
As investors, we will benefit if we are careful in our selection. A jobless growth economy creates challenges as well as opportunities.
Our Premium Members receive frequent updates on important and relevant economic factors that affect the stock market, industry sectors and individual stocks and ETFs. You should give our four-week free trial to the Premium Membership a try. There is no risk, nor any obligation. If you have any questions regarding membership, please send an email to [email protected] and we will get right back to you. Your complete satisfaction is of utmost importance to us.